Fintech Vs. Techfin: Where is the Future Headed?
Fintech Vs. Techfin: The Future of Finance and Banking
Recent years have seen a technological revolution in the financial sector, with new companies and emerging technology upending established business structures. FinTech and TechFin are concepts that are sometimes used interchangeably yet have clear distinctions. We will examine the differences between these two trendy terms and discuss how they will affect finance in the future in this blog article. Prepare to immerse yourself in the realm of digital money!
Describe FinTech
“Fintech,” or financial technology, refers to a broad class of tech firms that offer financial services and goods through technology. This can encompass everything from online lending platforms to mobile payments. FinTech firms frequently employ cutting-edge technology like blockchain and artificial intelligence to offer creative solutions to long-standing financial issues.
FinTech is a relatively new business yet has already experienced rapid expansion. FinTech companies saw record-breaking global funding in 2018 of $55 billion. As more individuals use digital financial solutions, this number is only anticipated to increase over the next several years.
Utilizing FinTech services has several advantages. They may provide customers with more ease, transparency, and security. They may give access to new markets and clients for enterprises. They can also promote inclusivity and economic progress for the whole population.
Describe TechFin.
The phrase “TechFin” refers to the fusion of technology and finance, which is relatively recent. New technologies are applied to financial services and products in this expanding industry.
TechFin businesses often employ technology to streamline financial procedures and generate fresh economic goods and services. For instance, a TechFin business may use blockchain technology to construct a new decentralized payment system or artificial intelligence (AI) to improve credit rating algorithms.
Many TechFin firms want to upend established financial institutions by providing more creative and effective solutions. However, a few TechFin businesses are assisting incumbents in modernizing their business practices.
The expansion of digital devices, the emergence of alternative finance, and the increased accessibility of robust and reasonably priced computer resources have all contributed to the growth of TechFin.
Advantages & Disadvantages of each
Advantages of FinTech:

- Innovation: FinTech companies are known for their ability to rapidly innovate and introduce new technologies and business models. This leads to the development of novel solutions that can improve efficiency, accessibility, and convenience in the financial services industry.
- Customer-centric approach: FinTech App companies often prioritize the needs and preferences of their customers, resulting in user-friendly interfaces, personalized experiences, and streamlined processes.
- Market disruption: FinTech has disrupted traditional financial institutions by offering alternative solutions that are often more affordable, efficient, and accessible. This has increased competition, leading to better services and pricing options for consumers.
- Enhanced financial inclusion: FinTech has the potential to extend financial services to underserved populations who may have limited access to traditional banking services, promoting financial inclusion and economic empowerment.
- Agility and flexibility: FinTech companies are typically more agile and adaptable compared to traditional financial institutions. This enables them to quickly respond to market demands, adjust their offerings, and scale their operations.
Disadvantages of FinTech:

- Regulatory challenges: The innovative nature of FinTech often poses regulatory challenges as traditional regulations may not be designed to address the unique business models and risks associated with these companies. Adhering to regulations while maintaining agility can be a complex task.
- Limited trust and credibility: Some consumers may have concerns about the security and reliability of FinTech services, especially when compared to long-established financial institutions with a solid track record. Building trust and credibility can be a challenge for newer FinTech players.
- Fragmented market: The FinTech industry is highly fragmented, with numerous players offering specialized services. This can lead to a fragmented user experience and the need for consumers to manage multiple accounts and platforms to access various financial services.
- Cybersecurity risks: The reliance on technology and online transactions exposes FinTech companies and their customers to cybersecurity threats. Protecting customer data and maintaining robust security measures is crucial but can be challenging in an evolving threat landscape.
- Limited product range: While FinTech companies have made significant strides in various financial sectors, their product range may still be limited compared to traditional financial institutions that offer a wide array of services under one roof.
Advantages of TechFin:
- Established technology infrastructure: TechFin companies, being traditional technology giants, have a strong foundation in terms of technology infrastructure, cloud computing capabilities, and data analytics expertise. This allows them to leverage existing resources to enhance financial services.
- Scale and market dominance: TechFin companies often have an extensive user base and established market dominance in their respective technology sectors. This provides them with a strong foundation to expand into finance and offer their financial services to a large user base.
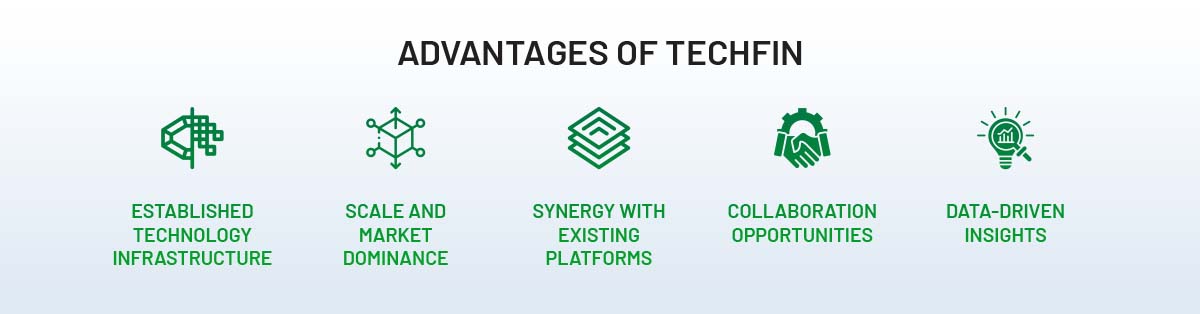
- Synergy with existing platforms: TechFin companies can seamlessly integrate financial services into their existing platforms, such as e-commerce, social media, or messaging apps. This offers a convenient and integrated experience for users, as they can access financial services within the platforms they already use.
- Collaboration opportunities: TechFin companies have the potential to collaborate with established financial institutions, leveraging their expertise in finance while bringing technological innovation to the table. This collaboration can lead to the development of new solutions that benefit both companies and consumers.
- Data-driven insights: With their expertise in data analytics, TechFin companies can leverage the vast amount of user data they possess to gain valuable insights. These insights can inform the development of tailored financial services, personalized experiences, and targeted marketing strategies.
Disadvantages of TechFin:
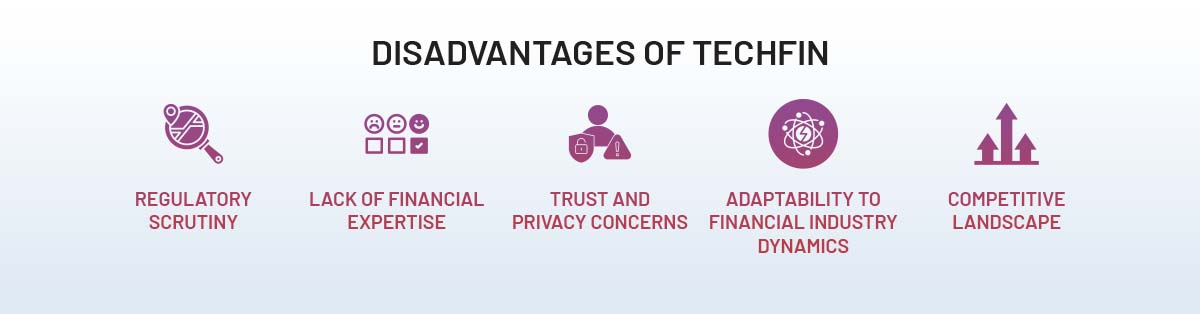
- Regulatory scrutiny: TechFin companies entering the finance sector often face enhanced regulatory scrutiny due to their market dominance and potential for disrupting traditional financial services. This can result in increased regulatory compliance requirements and oversight.
- Lack of financial expertise: While TechFin companies have strong technological capabilities, they may lack the deep understanding of financial systems and regulations that traditional financial institutions possess. This knowledge gap can present challenges when it comes to navigating complex financial regulations and ensuring compliance.
- Trust and privacy concerns: TechFin companies, especially those from the technology sector, may face trust and privacy concerns from consumers due to past incidents related to data breaches or misuse of personal information. Building trust and addressing privacy concerns are important considerations for TechFin companies entering the finance sector.
- Adaptability to financial industry dynamics: The financial industry operates under specific regulations, market dynamics, and risk management practices. TechFin companies may need to adapt their technology and business models to fit within these frameworks, which can require significant investment and time.
- Competitive landscape: TechFin companies entering the finance sector may face intense competition from both traditional financial institutions and existing FinTech players. Establishing a strong foothold and gaining market share in an already crowded space can be challenging.
Difference Between Fintech and TechFin
Although FinTech and TechFin both work at the nexus of finance and technology, there are significant distinctions in their historical contexts, methods, and areas of concentration. Let’s investigate how FinTech and TechFin compare in several areas:
| Aspect | FinTech | TechFin |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Companies that use technology to deliver financial services | Traditional technology companies entering the finance sector |
| Focus | Financial services | Technology and innovation in the finance sector |
| Origin | Emerged as startups disrupting traditional finance | Established technology companies expanding into finance |
| Core Competencies | Technological innovation, agility, and customer-centric approach | Technology infrastructure, data analytics, scalability |
| Services Offered | Payments, lending, investments, insurance, personal finance | Online platforms, cloud computing, data analytics, payments |
| Market Disruption | Disrupted traditional financial institutions | Challenging both traditional financial and technology sectors |
| Regulatory Impact | Regulatory challenges due to novel business models | Enhanced regulations due to increased market dominance |
| Collaboration | Collaborate with traditional institutions and regulatory bodies | Partner with established financial institutions |
| Customer Experience | Focus on user-friendly interfaces and seamless transactions | Seamlessly integrate financial services into daily activities |
| Innovation | Rapidly introduce new technologies and business models | Leverage existing technologies to enhance financial services |
| Competitive Advantages | Agility, innovation, and customer-centric approach | Extensive technology infrastructure, data analytics expertise |
| Examples | Stripe, Square, Robinhood, Ant Group, Revolut | Google Pay, Apple Pay, Amazon Pay, Tencent, WeChat Pay |
What separates fintech from techfin
Origin and Subject:
- FinTech: Startups specializing in utilizing technology to disrupt established financial services are known as fintech businesses. They want to solve the industry’s pain issues by offering creative solutions.
- The phrase “tech-fin” describes well-known technology companies that expand their product lines into the financial sector. Their primary objective is to enhance customer satisfaction and financial services by making greater use of the existing digital infrastructure.
Principal Competencies
- FinTech: FinTech businesses are known for their technology innovation, skill, and customer-centered outlook. When creating new financial solutions, they frequently put the user experience first and employ cutting-edge analytics and algorithms.
- TechFin: TechFin businesses have sophisticated technological infrastructure, knowledge of data analytics, and scalability. Utilizing current technology to improve financial services and provide seamless customer experiences is at the heart of their key strengths.
Services Provided
- FinTech: FinTech businesses offer various financial services, such as online payments, lending platforms, investing tools, insurance options, and personal finance management software. Within the finance sector, they concentrate on specialized areas.
- TechFin: TechFin enterprises integrate financial capabilities into their already-existing platforms, such as e-commerce, social networking, or messaging apps. They provide services, including online wallets, payment options, and financial infrastructure within these ecosystems.
Regulation Effect:
- FinTech: Due to their innovative business models, which do not conform to current regulatory frameworks, FinTech businesses frequently encounter regulatory issues. Regulators are trying to find a way to combine protecting consumers with promoting innovation.
- Due to their market dominance and potential to undermine established financial services, TechFin businesses that enter the finance industry may be subject to more stringent regulatory oversight. Increased restrictions may result from this examination to solve consumer protection, antitrust, and data privacy issues.
Collaboration:
- FinTech: To overcome regulatory obstacles, obtain resources, and grow their operations, FinTech businesses frequently work with established financial institutions and regulatory agencies. Through partnerships, they may benefit from the knowledge and resources of well-established players.
- TechFin: Businesses in the tech-fin sector may work with conventional financial institutions to bring their economic and technology know-how together. These partnerships may result in the creation of ground-breaking ideas that help both parties and provide better services to clients.
Client Experience
- User-friendly interfaces, smooth transactions, and customized experiences are priorities for fintech businesses. They work to make complicated financial procedures more user-friendly and accessible to benefit clients from improved convenience and empowerment.
- TechFin: TechFin businesses seek to easily incorporate financial services into their current platforms, enabling customers to trade inside the ecosystems they already interact with. This connection makes things more convenient and gives the user a consistent experience.
Innovation:
- FinTech: FinTech businesses are renowned for quickly bringing new technology to market and creating innovative business models. By utilizing cutting-edge technology like blockchain, machine learning, and artificial intelligence, they promote innovation in the financial sector.
- TechFin: TechFin businesses use their current infrastructure and technology to improve the quality of financial services and customer experiences.
Scalability and Reach:
- FinTech: Early-stage FinTech businesses frequently concentrate on specialized financial services or niche markets. Their flexibility and adaptability advantage, although having possibly restricted resources, enables them to adjust and grow their operations swiftly.
- TechFin: TechFin businesses benefit from already-existing, sizable user communities and well-established platforms, which extends their reach and enables them to roll out financial services to a sizable consumer base quickly. Their technological foundation and market domination frequently serve as the driving forces for their scalability.
Data and Analytics:
- The solutions provided by FinTech organizations are primarily reliant on data and analytics. They use user data, transactional data, and sophisticated analytics to offer customized financial services, personalized suggestions, and risk assessments.
- TechFin: Because of their enormous user bases and access to various data, TechFin businesses have tremendous data analytics capabilities. They apply data analytics to comprehend consumer behavior, preferences, and trends to provide relevant financial services within their ecosystems.
Though both work at the nexus of finance and technology, FinTech and TechFin have different histories, key capabilities, services provided, and market impacts. By bringing cutting-edge solutions, FinTech upends the financial sector, whereas TechFin uses existing infrastructure to improve financial services inside established ecosystems. Understanding the differences between these ideas is crucial to understanding how each one will affect finance in the future.
Future of Banking: Techfin vs. Fintech
At the nexus of FinTech and TechFin, where cutting-edge innovations and recognized technological titans are altering the financial environment, lies the future of banking. Let’s look at some prospective scenarios for banking in the future that both FinTech and TechFin will impact:
- Enhanced Digital Experience: As a result of FinTech and TechFin advancements, the banking sector will continue to prioritize digital experiences. Customers may anticipate more streamlined interactions across numerous digital channels, tailored services, and user-friendly interfaces. Digital wallets, individualized financial management tools, and mobile banking will all spread much further.
- AI and Automation: Significant changes in banking procedures will be brought about by AI and automation. Customers’ questions will be handled by chatbots and virtual assistants, who will also offer immediate assistance. AI algorithms will make more precise fraud detection, individualized financial advice, and credit evaluations possible. Back-office activities will be streamlined through automation, increasing productivity and lowering expenses.
- Collaboration and Open Banking: As open banking efforts spread, customers can safely exchange their financial information with different organizations. This will make it easier for conventional banks, FinTech startups, and TechFin enterprises to work together more often. New economic ecosystems will be created through partnerships and API connections, encouraging innovation and providing clients with broader services.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Data analytics and insights will play a significant role in banking’s future. Banks will use AI and machine learning algorithms to offer tailored financial products and services by utilizing massive volumes of client data. Data security and privacy will continue to be essential for banks navigating this data-driven environment.
- Blockchain and cryptocurrencies: Blockchain technology, which offers safe, open, and effective transactional methods, will keep up its disruption of the financial industry. Processes for trade financing, international payments, and identity verification will be made more accessible by distributed ledger technology. Introducing cryptocurrencies and Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) may also alter the banking industry’s infrastructure and payment methods.
Examples of Each Use
Applications of FinTech
- Digital Payments: Peer-to-peer payment networks, mobile wallets, and digital currencies have all been transformed by FinTech business models, allowing consumers to conduct safe and practical transactions.
- Online lending: FinTech lending platforms provide a variety of loan choices to both people and enterprises, utilizing cutting-edge algorithms to evaluate creditworthiness and expedite capital access.
- Robo-Advisory: Automated investment platforms using algorithms have been developed by FinTech to manage portfolios and offer individualized investment advice at a cheaper cost than traditional financial advisers.
- InsurTech: FinTech advancements in the insurance industry include automated claims processing, faster policy issuing, and tailored insurance products. These innovations increase productivity and improve client satisfaction.
- Personal Finance Management: FinTech solutions offer tools for budgeting, cost monitoring, and financial goal setting, helping users manage their finances better and make wise decisions.
Use Cases for TechFin:
- Digital wallets: TechFin firms use their current platforms to provide customers with digital wallet services, enabling smooth peer-to-peer and bill payment transactions inside their ecosystems.
- E-commerce Integration: TechFin businesses incorporate financial services into their e-commerce platforms, allowing customers to make payments, access financing alternatives, and manage orders without leaving the platform.
- Cloud-based Financial Infrastructure: TechFin firms use their strong cloud computing skills to offer safe and scalable financial infrastructure services to financial institutions, lowering costs and increasing operational effectiveness.
- Data analytics and insights: TechFin businesses employ extensive data analytics skills to examine consumer spending habits, market trends, and risk factors, giving financial institutions helpful information for product creation, marketing, and risk management.
- Open Banking: TechFin firms support programs that enable financial institutions to safely exchange consumer data through APIs, encouraging innovation and developing new financial services and partnerships.
Conclusion
The two different but closely linked industries of fintech and tech finance have grown in popularity recently. Both fields entail creating a Fintech app development company of digital goods and services that may be used to enhance financial operations, from processing payments to managing investments. Before deciding which area is best for you, it’s crucial to thoroughly evaluate your demands, as each one has its perks and drawbacks. FinTech or TechFin is a fantastic option for helping you achieve your business goals if the technological understanding and financial savvy are correctly balanced.
